Targeting apoptosis to induce mixed hematopoietic chimerism and long-term allograft survival without myelosupressive conditioning in mice.
Cippà PE, Gabriel SS, Chen J, Bardwell PD, Bushell A, Guimezanes A, Kraus AK, Wekerle T, Wüthrich RP, Fehr T. Blood 2013; 122:1669-1677.
Prepared by: Mansour Altayyar, Fall 2014
Layman Summary
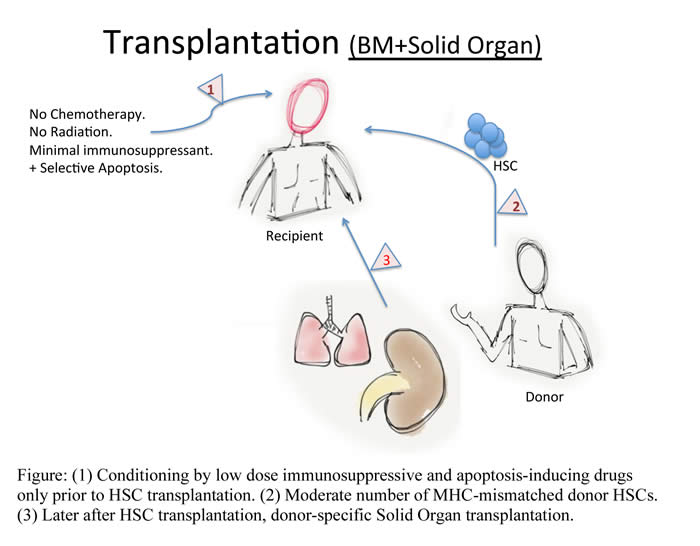
In the era of modern medicine, the goal of transplantation is to achieve effective therapies with minimal use of toxic drugs. This will enhance prognosis and lifestyle of patients by evading the current use of drugs. Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) has been used therapeutically for the treatment of non-solid cancers (leukemia and lymphoma) but also; there is a recent trend to use BMT to aid the transplantation of a solid organ. The organ will be from the same donor as the bone marrow cells. This will reduced the use of toxic drugs and lower immune rejection as well as suppress bone marrow function (Myelosupression).
After transplanting bone marrow and/or a graft, a mode of sickness may form as normal response to this transplantation that can lead to variable clinical manifestations known as graft-versus-host disease (GvHD). This would be caused by reactive immunological cells (T-Cells), which can eventually lead to graft rejection. The use of toxic drugs and radiation has proven to clear the cells responsible for the rejection. However, these drugs would also clear other types of cells that are important to maintain potent immunity. Thus, the scientists tested a new method to selectively clear only reactive cells by driving them into a programmed cell death (Apoptosis) using radiation-free protocol.
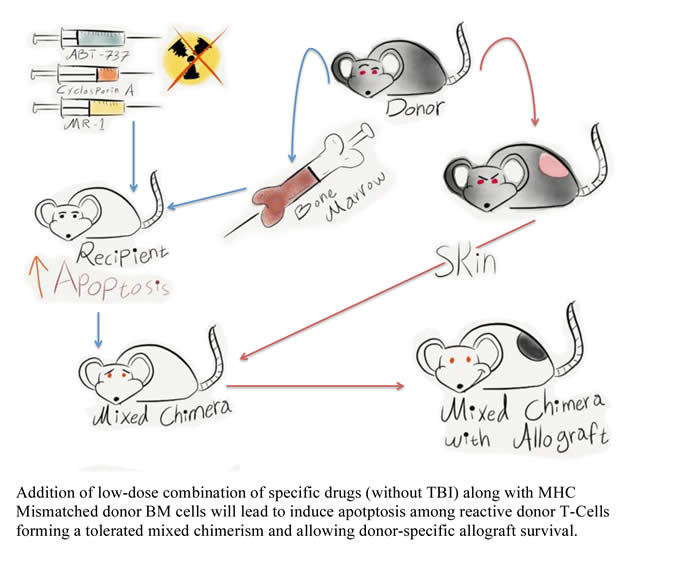
In their experiments, the researchers treated mice with a moderate dose of a drug that mimics the effect of a molecule that initiate cell death in reactive cells, the drug was called ABT-737. An immunosuppressive drug (Cyclosporin A) was added along ABT-737, which apparently enhanced its action; both drugs were started 3 days before BMT and discontinued at day 12 after BMT. A moderate number of bone marrow cells from a donor mouse were injected into a recipient mouse together with another molecule, which blocks reactive T-Cells. Testing the blood of the recipient mice revealed different Hematopoietic Cells within the same mouse. That is, the mice tolerated the cells from the donor along with its own; termed Mixed Chimerism.
The scientists took their findings further to determine if the chimeric mice can tolerate the skin of the donor cells. Along with this test, the scientists also use skin from a different mouse (3rd party). The researchers found that only skin grafts from the bone marrow donor mice survived over a long period of time, which made them conclude long-term durability of the mixed chimerism.
The article demonstrated a promising method of therapy in terms of solid organ transplantation with reduced toxic drugs, myelosupression and graft rejection. If such a method is translated into clinical use, it will be highly beneficial for patients who require organ transplant.
Scientific Summary
The purpose was to introduce a new approach to develop mixed hematopoietic chimerism by pharmacologically inducing intrinsic cascade of apoptosis in the reactive lymphocytes. By doing so, they plan to achieve stable tolerance and durability since this would allow for long-term donor specific allograft survival.
Since targeting apoptosis was the intended target of the study, the authors selected Bim (pro-apoptotic) as the main gene that drove reactive T-Cells (CD8) into apoptosis. In the absence of Bim, there was reduced chimera and decrease in allograft survival.
To stimulate Bim for induced apoptosis of reactive CD8+ cells, the authors used a small molecule, ABT-737 (BH3-only domain mimetic), in a moderate dose and a single injection of a single 2mg/kg dose of Co-stimulation Blockade (CSB) Anti-CD154 (MR1). This blocked T-cell activation by interrupting CD40-CD154 interaction, resulting in efficient induction of apoptotic cascades. The studies also showed that Bim expression could be blocked by Cyclosporin A (CsA). Although CsA could be anti-tolerigenic, it has an advantage due to its ability to block the effect of the apoptotic Bcl-2A1. Thus, the transplanted animals were give low-doses of CsA.
The experimental model used low-dose total body irradiation (TBI) and hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) transplantation into allogeneic recipient. After the hematopoietic transplant, the mice were given skin grafts from the other strain as well as from a third strain. At 33 weeks after the transplant there was evidence of tolerated mixed chimerism from mice treated with ABT-737 and CsA as compared to ABT-737. The authors concluded that ABT-737 reversed the anti-tolerogenic effect of CsA. It appeared that CsA enhanced the action of ABT-737.
Next the authors asked if they can still achieve mix chimerism without any myelosupression. They therefore excluded TBI and then repeated the studies. Although there was reduced numbers in the difference cell lineages, the results indicated that TBI could be eliminated to achieve mixed chimerism. The tolerance was maintained because alloreactive CD8 T-cells were deleted but the donor’s Antigen Presenting Cells (APC) were present.
Donor-specific skin graft survived in a radiation-free protocol and durability of this well-tolerated mixed chimerism. The tolerance was specific since a similar effect was not seen when the skin was obtained from a third party. Finally, the authors blocked the suppressive effect with CTLA4Ig and this led to immediate graft rejection, supporting a role for CD154/CD40-dependent mechanism of tolerance.
This paper provided a promising study for solid organ transplantation and to create a durable tolerance with mixed chimerism after BMT without any toxic or radiation based myelosupression. The method will allow for crossing over the MHC compatibility limitations. Further studies to ensure selectivity of alloreactive T-Cells apoptosis and durability of mixed chimerism without any maintenance by drugs could lead to the translation of the method.
|
