|
Tibor Rohacs, M.D., Ph.D. Office:(973) 972-4464 |
|
|
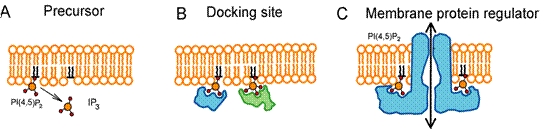
Regulation of ion channels by phosphoinositidesPhosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP 2 ) is a minor, but biologically important component of the plasma membrane. Its role was first appreciated as the precursor of IP 3 and DAG the two second messengers (A). Later it turned out that PIP 2 and other phosphoinositides serve as docking site for cytoplasmic signaling proteins, localizing them to the plasma membrane, where they exert their biological effects (B). Finally PIP 2 was shown to regulate an ever increasing number of transmembrane proteins, mainly ion channels and transporters (C). My laboratory focuses on PIP 2 regulation of one group of ion channels, the Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) channels.
TRP channels received a lot of attention recently, because of their involvement in a variety of important biological processes. Their function is remarkably diverse, they are involved in temperature sensation, mechanosensation, vision, taste, Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ transport across epithelial cells, apoptosis and Ca 2+ signaling by hormones and neurotransmitters. No common factor has emerged until recently that would underlie the regulation of TRP channels by such diverse stimuli. We suggest that PIP 2 may serve as such factor. The proximal C-terminal TRP domain, is the most conserved cytoplasmic region of TRP channels. The function of the TRP domain has been unknown until recently. We have found that PIP 2 activates TRPM8 and two other distantly related TRP channels through interacting with their TRP domain. These data suggests that PIP 2 is the common denominator of the regulation of TRP channels. Our laboratory focuses on understanding how phosphoinositides regulate TRP channels, and what the physiological importance of this regulation is.
• Rohács T , Lopes CMB, Michailidis I and Logothetis DE . PI(4,5) 2 regulates theactivation and desensitization of TRPM8 channels through the TRP domain. Nature Neuroscience 8: 626-634, 2005. • Rohács T . Teaching Resource. TRP channels. Sci STKE 2005: tr14, 2005. • Rohács T , Lopes CM, Jin T, Ramdya PP, Molnar Z and Logothetis DE. Specificity of activation by phosphoinositides determines lipid regulation of Kir channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 745-750, 2003. • Zhang H, Craciun LC, Mirshahi T, Rohács T , Lopes CMB, Jin T and Logothetis DE. PIP 2 activates KCNQ channels and its hydrolysis underlies receptor-mediated inhibition of M currents. Neuron 37: 963-975, 2003. • Lopes CMB, Zhang H, Rohács T , Jin T and Logothetis DE . Alterations in Conserved Kir Channel-PIP 2 Interactions Underlie Channelopathies. Neuron 34: 933-944, 2002. • Rohács T , Lopes C, Mirshahi T, Jin T, Zhang H and Logothetis DE. Assaying phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate regulation of potassium channels. Methods Enzymol 345: 71-92, 2002. • Rohács T , Chen J, Prestwich GD and Logothetis DE. Distinct specificities of inwardly rectifying K + channels for phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem 274: 36065-36072, 1999. |
|