|
|
 |
 |
|
THYROID: TOXIC GOITER, TREATED
PERTINENT CHANGES: |
 |
 |
|
- The thyroid gland has an uneven appearance.
- Some segments of thyroid glands contain follicles with little or no colloid in their lumens.
- Colloid when present is scant, thin and light blue in appearance.
- Most of these follicles are lined by tall columnar cells.
- In areas the epithelium is thrown up into papillary projections.
- Some groups of follicles are filled with pink colloid and are lined by flattened or cuboidal epithelial cells.
- No interstitial fibrosis is present.
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
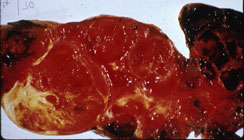
A. Gross cut surface view of a nodular goiter. Note nodules of varying size and partial encapsulation. Compare with the next image of diffuse goiter. |
|
|
|
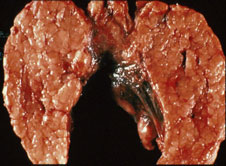
B. Gross cut surface view of diffuse toxic goiter. The gland is relatively homogeneous, and is diffusely enlarged. |
|
|
|
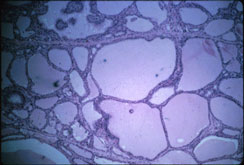
C. Low power microscopy shows some variability in follicle size due to iodine treatment with some follicles containing colloid. |
|
|
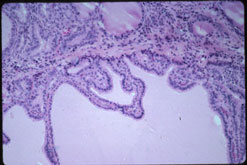
D. High power shows some thyroid hyperplasia with mild infolding of high cuboidal thyroid follicle cells. |
|
|
|